EDUCATION
Intensive Property: Understanding Its Role in Science and Beyond
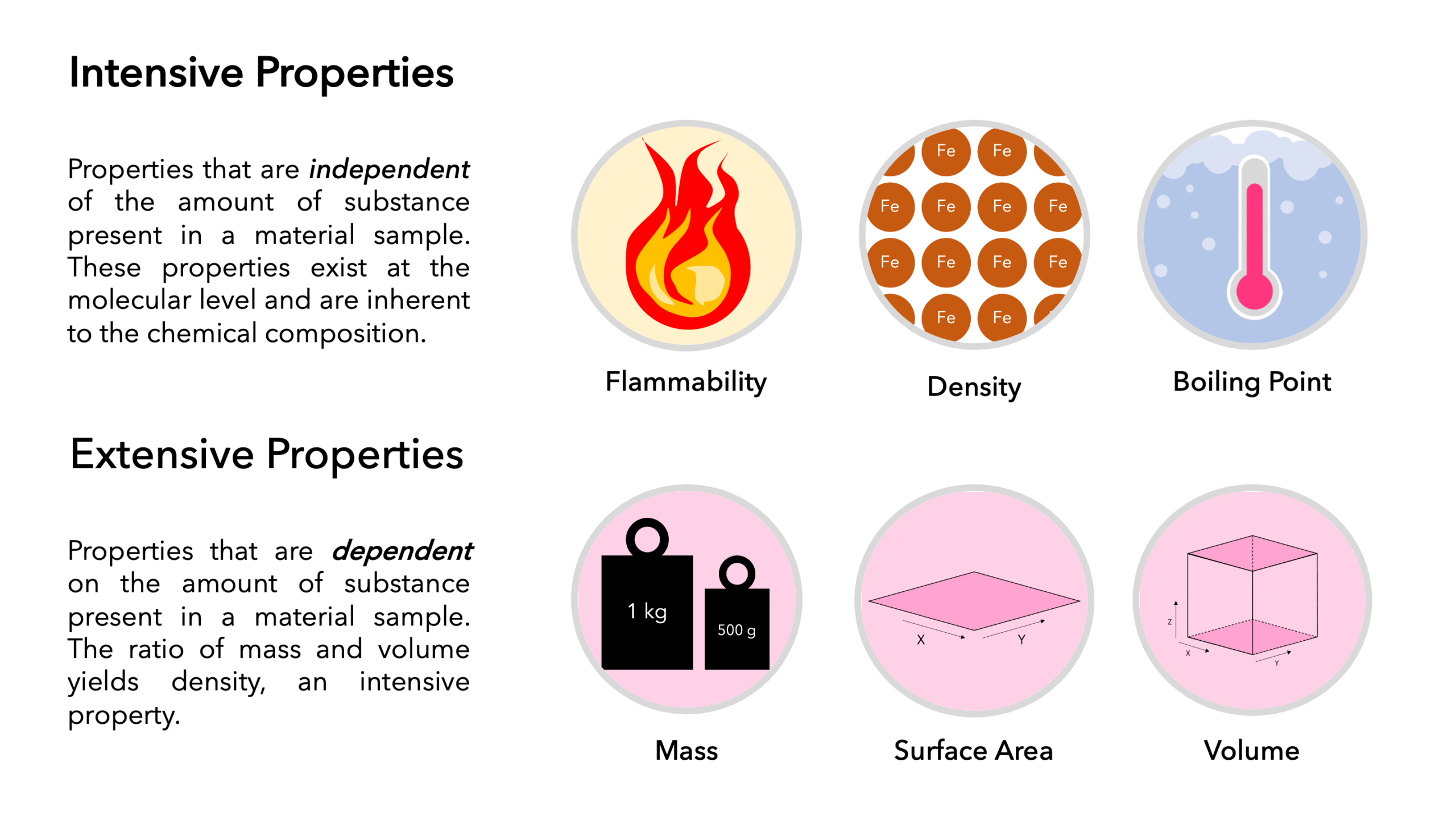
Every scientific field has foundational concepts that serve as building blocks for deeper understanding. Among these, the intensive property stands out as one of the most crucial. Whether in chemistry, physics, or engineering, intensive properties allow us to define, analyze, and predict material behaviors without being influenced by quantity.
This blog post will educate readers about the role of intensive property, its applications, benefits, and why it remains central to modern science and industry.
What is an Intensive Property?
An intensive property is a physical property of matter that does not depend on the amount of substance present. Unlike extensive properties (such as mass, volume, or length), intensive properties remain constant regardless of how much material you have.
Examples of Intensive Properties:
-
Temperature
-
Pressure
-
Density
-
Color
-
Melting point
-
Boiling point
Therefore, no matter if you have one drop of water or an entire ocean, its temperature and boiling point remain the same under identical conditions.
Importance of Intensive Properties in Science
Intensive properties are vital because they:
-
Define Material Identity – Density and boiling points help identify substances.
-
Standardize Comparisons – They allow fair comparison of materials regardless of sample size.
-
Support Theoretical Models – Thermodynamics heavily relies on intensive properties.
- Guide Industrial Processes – In chemical and mechanical industries, they regulate design and safety.
Key Benefits of Intensive Properties
-
Consistency: Remains unchanged by size, ensuring reliable measurements.
-
Identification: Supports accurate classification of substances.
-
Efficiency: Simplifies experiments by reducing variable factors.
-
Predictability: Enhances accuracy in forecasting reactions and material behavior.
Applications of Intensive Properties in Modern Society
1. Chemistry and Materials Science
-
Identifying unknown compounds by density or boiling point.
-
Designing alloys with specific hardness and melting points.
2. Physics and Thermodynamics
-
Calculating equilibrium conditions.
-
Defining state functions like pressure and temperature.
3. Engineering and Industry
-
Quality control using refractive index.
-
Safety checks using flash point and boiling point data.
4. Everyday Life Applications
-
Cooking: boiling water temperature is independent of pot size.
-
Medicine: concentration of drugs remains constant per dose.
Practical Tips for Using Intensive Properties
-
Use Ratios Wisely – Divide extensive by extensive (e.g., mass/volume = density).
-
Check Conditions – Temperature and pressure affect many intensive properties.
-
Rely on Reference Tables – Use trusted data sources for accurate values.
-
Apply in Quality Control – Compare sample measurements against standards.
Personal Anecdote: My First Encounter with Intensive Property
As a chemistry student, I once miscalculated a solution by assuming that doubling the amount of solute would double its concentration. My professor explained that concentration is an intensive property—it doesn’t change with the sample size as long as proportions remain the same. That realization helped me better understand laboratory practices and avoid costly mistakes later in research.
Also Read: Tatasec.org: Understanding Its Role
Intensive Properties in the Modern Era
Today’s scientific and industrial world heavily depends on intensive properties:
-
Sustainability: Industries monitor intensive properties to minimize waste.
-
Innovation: Material engineers create advanced composites based on melting points and densities.
-
Global Standards: Intensive properties like temperature ensure universal scientific communication.
Suggested Visuals
-
Landscape Image: A laboratory setting with instruments measuring temperature and density.
-
Chart/Infographic: Comparison table of intensive vs. extensive properties.
-
Diagram: Applications of intensive properties across industries.
Conclusion
Intensive properties may seem simple, but they are the cornerstones of science and industry. By providing consistency, reliability, and predictability, they empower researchers, engineers, and everyday individuals to make informed decisions.
FAQs
What makes a property intensive?
A property is intensive if it remains unchanged regardless of the amount of substance present.
How do intensive and extensive properties differ?
Intensive properties are independent of size, while extensive ones depend on the sample amount.
Why are intensive properties important in chemistry?
They help identify substances and maintain consistency in experiments.
Can an intensive property become extensive?
Yes, when combined (e.g., total heat capacity), intensive properties can contribute to extensive ones.
What are common intensive properties used in industry?
Density, refractive index, melting point, and viscosity are widely used.
How do intensive properties help in daily life?
They ensure cooking, medicine, and environmental processes remain predictable and consistent.
Where can I learn more?
Academic textbooks, journals, and resources like the American Chemical Society and university research guides.

-

 ENTERTAINMENT3 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT3 months agoBuilding Community Through Compassion: The Social Mission Behind Big Yard’s Music
-

 GUIDE3 months ago
GUIDE3 months agoBenefits of Air Casters for Safe and Efficient Material Handling
-

 HOME IMPROVEMENT2 months ago
HOME IMPROVEMENT2 months agoWall Panels: Transforming Spaces with Style and Functionality
-

 GUIDE2 months ago
GUIDE2 months agoBuild to Suit Opportunities Offer Turnkey Locations for Retail Business